Introduction
Climate change is one of the most pressing issues facing our planet today. As global temperatures rise, the effects on our environment, economies, and societies become increasingly severe. This blog aims to provide a comprehensive overview of climate change, its causes, impacts, and the latest efforts to mitigate its effects.
What is Climate Change?
Climate change refers to significant changes in global temperatures and weather patterns over time. While climate change is a natural phenomenon, scientific evidence shows that human activities have been the dominant cause of the observed warming since the mid-20th century.
Causes of Climate Change
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: The burning of fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) for energy and transportation releases large amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, leading to a greenhouse effect.
- Deforestation: Trees absorb CO2, and when they are cut down, this carbon is released back into the atmosphere. Deforestation also reduces the planet's capacity to absorb future emissions.
- Industrial Processes: Certain industrial activities release greenhouse gases like methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O).
- Agriculture: Agricultural practices, especially livestock farming, produce significant amounts of methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
Impacts of Climate Change
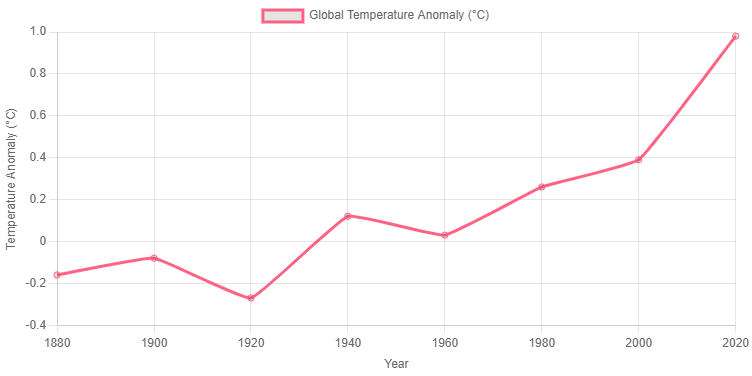
- Rising Temperatures: The average global temperature has increased by approximately 1.2°C (2.2°F) since the late 19th century. This rise is associated with more frequent and severe heatwaves.
- Melting Ice Caps and Rising Sea Levels: The polar ice caps and glaciers are melting, contributing to rising sea levels. This threatens coastal communities and ecosystems.
- Extreme Weather Events: Climate change increases the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, including hurricanes, floods, droughts, and wildfires.
- Ocean Acidification: Increased CO2 levels are absorbed by the oceans, leading to acidification. This affects marine life, particularly coral reefs and shellfish.
- Biodiversity Loss: Many species are unable to adapt quickly enough to the changing climate, leading to habitat loss and extinction.
Current Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
- Renewable Energy: Transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydropower reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
- Energy Efficiency: Improving energy efficiency in buildings, transportation, and industries can significantly lower emissions.
- Reforestation and Afforestation: Planting trees and restoring forests can absorb CO2 from the atmosphere.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Practices like crop rotation, conservation tillage, and improved livestock management can reduce emissions from agriculture.
- Policy and Legislation: Governments worldwide are implementing policies to reduce emissions, such as carbon pricing, emission trading systems, and subsidies for clean energy.
- Climate Resilience: Building resilient infrastructure and developing early warning systems can help communities adapt to climate impacts.
The Role of International Agreements
- The Paris Agreement: Adopted in 2015, this landmark accord aims to limit global warming to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels, with efforts to limit the increase to 1.5°C.
- COP26 and COP27: These conferences have seen nations commit to more ambitious climate targets, with a focus on reducing emissions, adapting to climate impacts, and financing climate action.
The Latest Developments (2024)
- Technological Innovations: Advances in carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology, as well as breakthroughs in renewable energy storage, are promising to accelerate emission reductions.
- Climate Finance: Increased funding for climate action, particularly for developing nations, is helping to address both mitigation and adaptation needs.
- Global Climate Summits: Recent summits have seen enhanced commitments from major economies, including net-zero targets and significant investments in green infrastructure.
- Public Awareness and Activism: Growing public awareness and activism are driving political and corporate action on climate change.
Conclusion
Climate change is a complex and multifaceted challenge that requires immediate and sustained action from individuals, businesses, and governments worldwide. By understanding its causes and impacts, and by supporting and implementing effective mitigation and adaptation strategies, we can work together to protect our planet for future generations.
Call to Action
Stay informed about climate change and support policies and practices that reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Small actions, when multiplied across communities and nations, can make a significant difference.
Learn More About Climate Action